Forecast Period | 2026-2030 |
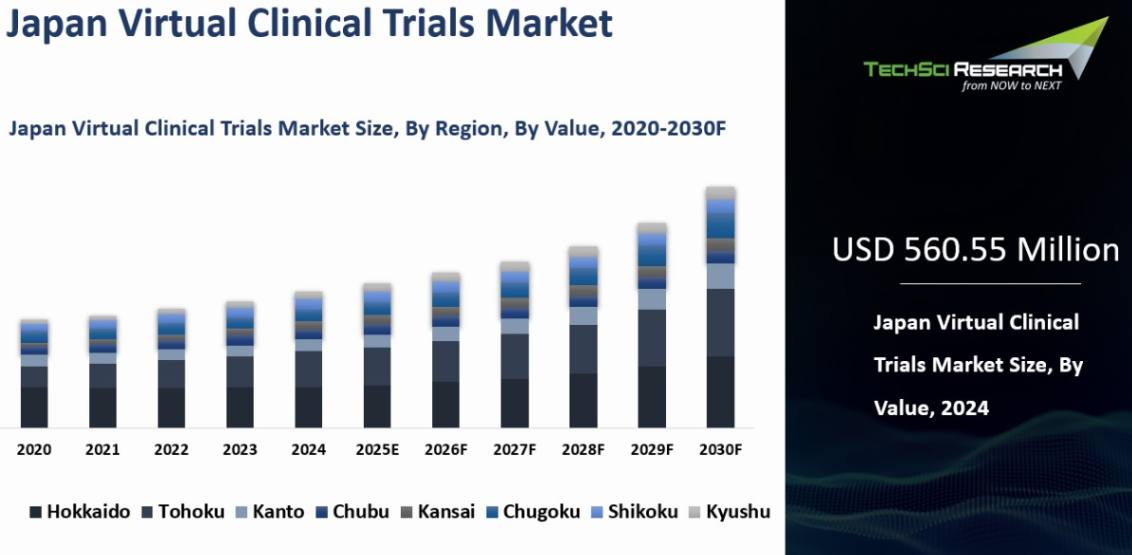
Market Size (2024) | USD 560.55 Million |
Market Size (2030) | USD 772.51 Million |
CAGR (2025-2030) | 5.45% |
Fastest Growing Segment | Oncology |
Largest Market | Kanto |
Market Overview
Japan
Virtual Clinical Trials Market was valued at USD 560.55 Million in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 772.51 Million with a CAGR of 5.48% through 2030.
The Japan Virtual Clinical Trials (VCT) market is rapidly
evolving due to advancements in technology, regulatory developments, and
shifting industry trends. This market is experiencing significant growth driven
by the increasing demand for flexible and efficient clinical trial
methodologies. Pharmaceutical companies, biotechnology firms, and research
organizations are leveraging virtual trial capabilities to enhance efficiency,
reduce costs, and improve patient recruitment and retention. Industry reports
project continued robust growth, supported by technological advancements and an
evolving regulatory landscape. Despite challenges, the future outlook for the
Japan VCT market is positive, with ongoing innovation and adaptation expected
to drive further expansion and success.
Download Free Sample Report
Key Market Drivers
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements are central to the growth of Japan’s Virtual Clinical Trials (VCT) market, improving trial efficiency, reach, and accuracy through digital integration. Wearable devices and sensors now enable real-time monitoring of patient vitals such as heart rate, blood pressure, and glucose levels, a capability especially critical in oncology, the dominant VCT indication in 2024. This continuous data collection allows researchers to assess health and treatment outcomes remotely, enhancing data precision and patient safety.
Mobile health (mHealth) applications further drive VCT adoption by allowing patients to record and share health data, complete remote assessments, and communicate with healthcare teams. These platforms streamline data collection and increase engagement by offering easy access to trial activities. Government initiatives rolling out nationwide e-prescription, welfare data integration, and hospital digital transformation advanced through permanent telemedicine rules established in October 2020 and expanded digital health policies in 2025 are strengthening infrastructure and supporting virtual trials.
Telemedicine platforms have become key to remote clinical engagement, offering secure video consultations, messaging, and follow-ups that reduce physical visits. National guidance allowing remote consultations issued in April 2020 and formalized as permanent in October 2020 underpins VCT workflows at scale. eConsent systems have digitized the consent process, enabling faster, more compliant, and paperless documentation for decentralized and hybrid designs. These tools enhance trial accessibility and participation, particularly for patients in remote areas.
Advances in artificial intelligence and data analytics now enable real-time analysis of large datasets, helping identify patterns, refine protocols, and predict outcomes. Predictive analytics also allows dynamic trial adjustments, improving flexibility and safety in decentralized settings. Interoperability among systems such as electronic health records (EHRs), clinical trial management systems (CTMS), and remote monitoring tools ensures seamless data flow and reduces errors.
Data integrity and security technologies, including stronger cybersecurity controls aligned with regulatory expectations, are being adopted to secure trial data through tamper‑resistant records, ensuring transparency and trust. Together, these innovations are reshaping Japan’s clinical research landscape, making trials more efficient, patient‑centric, and data‑driven.
Patient-Centric Trends
Patient-centric trends are key to the growth of Japan’s Virtual Clinical Trials (VCT) market, as they focus on improving patient experience and engagement. Virtual trials offer convenience and flexibility by reducing the need for frequent site visits, allowing patients with mobility challenges, tight schedules, or remote locations to participate from home, reflected in telehealth users rising from 13,618 to 28,853 across study periods spanning before and after April 2020. Remote data collection and virtual consultations align with patients’ preferences for managing health on their terms, with monitoring device use growing from 707 to 2,511 and prescription support recorded in 26,494 telehealth cases after April 2020, improving satisfaction and participation.
Enhanced transparency and communication are central to patient-centric virtual trials. Digital platforms enable regular updates, feedback, and two-way interaction between patients and researchers, supported by national guidance on eConsent and electronic explanations in clinical trials issued in March 2023. Personalized care is another major advantage, with a JPMA survey of 69 companies yielding 52 responses and identifying 13 companies that had run eConsent trials and 17 such trials during or after 2020, enabling protocol adjustments tailored to individual needs. This personalization improves outcomes and engagement while making participation more relevant.
Virtual trials also expand accessibility by removing geographical barriers, allowing broader and more diverse patient recruitment, evidenced by out-of-prefecture telehealth services increasing from 455 to 766 and participating medical institutions increasing from 1,007 to 1,392 after April 2020. Greater inclusivity enhances the quality and applicability of research results. Convenience, reminders, and virtual check-ins help maintain engagement and reduce dropout rates, with average telehealth use per patient increasing from 1.41 to 2.26 visits in the same analysis.
By streamlining participation through digital tools such as remote monitoring, virtual assessments, and medication adherence reminders, virtual trials lessen the physical and emotional burden on patients, alongside the rollout of e-prescriptions across 4,690 facilities as of July 2023, including 4,229 pharmacies, 423 medical clinics, 24 dental clinics, and 14 hospitals. These features support adherence to trial protocols and simplify health management, improving both the experience and data quality, as reinforced by PMDA guidance on digital tools in trials and nationwide telemedicine implementation lists published in April 2020.
As patients increasingly expect research models that prioritize comfort and accessibility, virtual trials meet these expectations by offering patient-friendly processes and ongoing feedback mechanisms established in PMDA digital trial guidance and eConsent policies. Incorporating patient input enables researchers to refine trial designs, strengthen relationships, and ensure responsiveness to participant needs, reinforcing VCT adoption across Japan’s evolving healthcare landscape as remote care infrastructure and provider participation expand.
Advances in Data Analytics
Advances in data analytics are a major factor driving growth in Japan’s Virtual Clinical Trials (VCT) market. These advancements improve trial efficiency, scalability, and accuracy through sophisticated data management and analysis. Digital health tools such as wearables and remote monitoring devices enable continuous data collection and real-time analysis of patient health, treatment response, and adverse events. This constant data flow allows researchers to adjust protocols promptly, ensuring trials stay aligned with objectives and improving overall responsiveness.
Unified data platforms now integrate information from electronic health records (EHRs), remote monitoring tools, and patient-reported outcomes, providing a comprehensive view of each participant. Improved interoperability and standardized data formats enable seamless data exchange between systems, streamlining data collection and analysis. Advanced analytics techniques such as multivariate analysis, Bayesian modeling, and machine learning reveal complex patterns and correlations, enhancing researchers’ ability to detect significant effects and refine trial design.
Predictive analytics powered by AI helps forecast patient responses, identify risks, and optimize trial parameters. This foresight allows researchers to make proactive adjustments and improve trial efficiency. Data analytics also supports precision medicine by using patient-specific data such as genetic profiles and biomarkers to tailor treatments, improving relevance and effectiveness. Enhanced patient stratification based on demographic, clinical, and genetic data helps identify subgroups likely to respond better to targeted therapies.
Automated data validation and quality control tools detect inconsistencies and errors in real time, ensuring accuracy and reliability. Strengthened data security through encryption, access controls, and regulatory compliance safeguards patient privacy and fosters trust. Together, these advancements make Japan’s virtual clinical trials more adaptive, data-driven, and patient-focused, accelerating progress toward more personalized healthcare solutions.
Key Market Challenges
Regulatory and Compliance
Issues
Navigating
the regulatory landscape for virtual clinical trials in Japan can be complex.
Although regulatory bodies like the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency
(PMDA) are evolving their frameworks to accommodate virtual trials, there
remains a lack of standardized guidelines specifically tailored to VCTs. This
complexity can create uncertainty and hinder the adoption of virtual trials, as
sponsors and researchers must ensure compliance with various regulations
related to data security, patient consent, and trial conduct.
Virtual
trials involve the collection, storage, and transmission of sensitive health
data, which raises significant data privacy and security concerns. Ensuring
compliance with stringent data protection regulations, such as the Act on the
Protection of Personal Information (APPI) in Japan, is critical. The need for
robust cybersecurity measures and data handling protocols can be a barrier for
organizations looking to implement virtual trials, as they must invest in
advanced technologies and practices to safeguard patient information.
Technological and
Infrastructure Limitations
The
success of virtual clinical trials depends heavily on the availability and use
of digital health technologies by both patients and clinical sites. In Japan,
there is variability in technological access and digital literacy among
different patient populations. This disparity can affect patient participation
and engagement, particularly in rural or underserved areas where access to
high-speed internet and advanced digital devices may be limited. Ensuring that
all potential participants have the necessary technology and skills to engage
in virtual trials remains a significant challenge.
Virtual
trials require seamless integration of various digital tools and platforms,
including electronic health records (EHRs), remote monitoring devices, and
telemedicine systems. Achieving interoperability between these systems can be
challenging due to differences in technology standards and data formats. The
lack of standardized protocols for data exchange and integration can hinder the
efficiency and effectiveness of virtual trials, impacting data accuracy and
trial outcomes.
Patient and Investigator
Engagement
While
virtual trials offer convenience, they also face challenges in recruiting and
retaining participants. Patients may be hesitant to participate in virtual
trials due to concerns about the quality of remote care, the unfamiliarity of
virtual platforms, or a lack of access to necessary technology. Additionally,
the need for patients to self-manage their participation and provide accurate
data remotely can be a barrier to engagement, particularly for those with
limited digital literacy or technical support.
Clinical
investigators and site staff need to adapt to new virtual trial methodologies
and technologies. This adaptation involves significant training and adjustment
to ensure they can effectively manage remote patient interactions, data
collection, and trial oversight. The transition from traditional to virtual
trial methods can be challenging, particularly for investigators who are
accustomed to in-person interactions and manual processes. Ensuring that
investigators are adequately trained and supported is essential for the
successful implementation of virtual trials.
Key Market Trends
Advancements in Digital Health
Technologies
The
rapid evolution of digital health technologies, including wearables and remote
monitoring tools, is a major driver of growth in the VCT market. These
technologies enable continuous and real-time monitoring of patient health
metrics, such as vital signs, activity levels, and biometric data. By providing
precise and ongoing data collection, they enhance the ability to track patient
responses to treatments and adjust protocols dynamically. The adoption of these
tools is making it easier to conduct complex trials, particularly for chronic
and long-term conditions, and supports the shift towards decentralized and
patient-centric research models.
The
increased use of telemedicine platforms and virtual consultations is also
contributing to the growth of VCTs. These platforms facilitate remote
interactions between patients and healthcare professionals, allowing for
regular check-ups, consultations, and follow-up appointments without the need
for physical visits. This trend not only improves patient convenience but also
extends the reach of clinical trials to a broader patient population, including
those in remote or underserved areas. The integration of telemedicine into VCTs
helps streamline trial processes and reduce operational costs.
Regulatory Evolution and
Support
Regulatory
bodies in Japan, such as the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA),
are increasingly adapting their frameworks to accommodate and support virtual
clinical trials. This includes the development of guidelines that address the
unique challenges and requirements of VCTs, such as data security, remote
patient monitoring, and digital consent. The growing acceptance and endorsement
of virtual trial methodologies by regulatory agencies are facilitating smoother
approvals and encouraging more sponsors to pursue VCTs.
As
virtual trials involve the collection and management of sensitive health data,
there is a strong focus on ensuring data integrity and security. Advances in
cybersecurity measures and data management practices are addressing these
concerns and enhancing the credibility of VCTs. By implementing robust security
protocols and compliance measures, regulatory bodies are fostering an
environment where virtual trials can be conducted with confidence in data
protection and regulatory adherence.
Increased Focus on
Patient-Centric Approaches
There
is a growing emphasis on patient-centric approaches in clinical research, which
prioritizes the needs and preferences of patients. Virtual trials align well
with this trend by offering greater convenience and flexibility, thereby
improving patient engagement and recruitment. By reducing the need for frequent
site visits and accommodating patients’ schedules, virtual trials make
participation more accessible and appealing. This patient-centric model not
only boosts enrollment rates but also enhances the overall quality and
reliability of trial data.
The
rise of personalized and precision medicine is driving the need for more
targeted and individualized clinical trials. Virtual trials are well-suited to
this trend as they enable the integration of advanced diagnostic tools and
genetic information to tailor treatments to specific patient profiles. The
ability to conduct remote assessments and monitor individualized treatment
responses supports the development of more precise and effective therapies. As
personalized medicine continues to advance, the demand for virtual trials that
can accommodate these sophisticated approaches is expected to grow.
Segmental Insights
Indication Insights
Based
on the category of Indication, the Oncology segment emerged as the dominant in the
market for Japan Virtual Clinical Trials in 2024. Oncology trials often involve
complex protocols and a need for precision in patient monitoring and data
collection. Virtual clinical trials cater to these needs by enabling remote
patient monitoring, which is crucial for tracking the progression of cancer and
the effects of treatment in real-time. This capability is particularly
beneficial for oncology, where continuous and precise data is required to
assess treatment efficacy and patient responses. The oncology sector is one of
the most active areas in clinical research, with numerous ongoing studies aimed
at developing new therapies and targeted treatments. The demand for innovative
treatments drives the need for efficient trial designs, including virtual
trials. The ability to reach a broad patient population and gather extensive
data remotely aligns well with the needs of oncology research, where patient
participation is critical.
Oncology
trials often require significant patient enrollment due to the need for large
sample sizes to ensure statistically significant results. Virtual clinical
trials facilitate broader patient recruitment by overcoming geographical
barriers and enabling participation from remote locations. This expanded reach
is essential for oncology trials, which frequently involve patients with
specific cancer types or stages, who may be dispersed across various regions. Cancer
patients often face physical challenges and constraints that make frequent
visits to clinical sites difficult. Virtual trials offer the flexibility and
convenience of remote participation, reducing the burden on patients who are
undergoing cancer treatment. This patient-centric approach improves enrollment
and retention rates, which are critical for the success of oncology trials. Oncology
trials generate vast amounts of data related to biomarkers, genetic
information, and treatment responses. Virtual trials leverage advanced data
management systems to handle and analyze this data efficiently. The ability to
integrate various data sources and perform real-time analysis enhances the
overall effectiveness of oncology research and accelerates the development of
new treatments. These factors collectively contribute to the growth of this
segment.

Download Free Sample Report
Regional Insights
Kanto
emerged as the dominant in the Japan Virtual Clinical Trials market in 2024,
holding the largest market share in terms of value. The Kanto Region is home to
Japan’s largest concentration of biopharmaceutical companies, clinical research
organizations (CROs), and contract research organizations (CROs). This
concentration provides a robust ecosystem that supports the development and
execution of virtual clinical trials. The presence of these organizations
ensures access to a skilled workforce, advanced technology, and extensive
research networks, all of which are crucial for the successful implementation
of VCTs. The Kanto Region benefits from a highly developed technological
infrastructure, including high-speed internet and advanced data management
systems.
This technological edge facilitates the implementation of virtual
trial protocols, which rely heavily on digital tools for data collection,
patient monitoring, and remote consultations. The region's technological
readiness supports the seamless execution of virtual trials and attracts
companies seeking a reliable environment for their clinical studies. The Kanto
Region, particularly Tokyo, is the epicenter of regulatory oversight in Japan.
The presence of the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) and other
regulatory bodies ensures that virtual clinical trials conducted in this region
adhere to stringent standards and guidelines. This regulatory rigor enhances
the credibility and acceptance of VCTs, making the region a preferred choice
for sponsors looking to ensure compliance with both Japanese and international
regulations.
The
Kanto Region has a large and diverse population, providing a substantial
patient pool for clinical trials. The region’s high population density and
diverse demographics facilitate easier patient recruitment and retention for
virtual trials. This is particularly advantageous for studies requiring
specific patient profiles or large sample sizes. The Japanese government and
local authorities in the Kanto Region offer various financial and research
incentives to encourage the growth of clinical research and innovation. These
incentives include funding opportunities, tax breaks, and grants for companies
engaged in clinical research, including virtual trials. Such support reduces
the financial burden on trial sponsors and enhances the region’s attractiveness
as a hub for VCTs.
Recent Developments
- In January 2025, Telemedicine Technologies entered a CRO Alliance with Micron (Japan), integrating the CleanWeb eClinical suite (eConsent, ePRO, CTMS, eTMF/eISF, remote monitoring, rSDV, imaging) with Micron’s local presence to expand decentralized trial operations and imaging-enabled virtual workflows across Asia and Japan.
- In March 2025, MHLW announced a six-point plan to strengthen Japan’s clinical research infrastructure, emphasizing decentralized and data-driven trials, centralized IRBs, validated digital platforms, and real-world data use in submissions to reduce drug lag and lower trial costs.
- In April 2025, industry briefings outlined Japan-specific remote monitoring requirements and operational nuances from PMDA that sponsors must address when deploying DCT platforms and services for Japanese sites and patients.
- In May 2025, policy analyses noted that Japanese regulatory documents from 2024 were moving into practice, offering direction on the use of remotely collected data and supporting eConsent adoption, which in turn spurred pilot programs for hybrid and virtual trials in oncology and specialty areas.
- In May 2025, national media also reported preparations for the world’s first clinical trial of artificial blood by March 2025, showcasing Japan-centered operational innovation; although not fully virtual, the initiative reflected rising national interest in new trial models and digital processes.
- In June 2025, a broad regulatory update underscored intensified reforms to accelerate access and modernize trials, introducing clear measures to support decentralized trials, risk-based inspections, and technology adoption to improve oversight and data integrity.
- In
April 2020, The Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (MHLW) issued guidance
on the Timely/Exceptional Handling of Consultations Using Telephones and Other
Telecommunication Equipment due to the spread of novel coronavirus infections.
This guidance was formalized into permanent regulations in October 2020.
Consequently, new clinical trial methodologies that do not require in-person
patient visits to medical institutions, such as Decentralized Clinical Trials
(DCTs) and Virtual Clinical Trials (VCTs), are increasingly being implemented
in Japan.
Key Market Players
- ICON,
plc
- Parexel International (MA) Corporation
- IQVIA Inc
- Laboratory Corporation of America®
Holdings
- LEO Innovation LabLEO Innovation Lab
- Medidata
- Oracle
- NOW Foods
- Medable Inc
- CROPRIME Ltd
|
By
Study
|
By
Indication
|
By
Phase
|
By
Region
|
- Interventional
- Observational
- Expanded
Access
|
- CNS
- Autoimmune/Inflammation
- Cardiovascular
Disease
- Metabolic/Endocrinology
- Infectious
Disease
- Oncology
- Genitourinary
- Ophthalmology
- Others
|
- Phase
I
- Phase
II
- Phase
III
- Phase
IV
|
- Hokkaido
- Tohoku
- Kanto
- Chubu
- Kansai
- Chugoku
- Shikoku
-
Kyushu
|
Report Scope:
In this report, the Japan Virtual Clinical Trials
Market has been segmented into the following categories, in addition to the
industry trends which have also been detailed below:
- Japan Virtual Clinical Trials Market, By Study:
o Interventional
o Observational
o Expanded Access
- Japan Virtual Clinical Trials Market, By Indication:
o CNS
o Autoimmune/Inflammation
o Cardiovascular Disease
o Metabolic/Endocrinology
o Infectious Disease
o Oncology
o Genitourinary
o Ophthalmology
o Others
- Japan Virtual Clinical Trials Market, By Phase:
o Phase I
o Phase II
o Phase III
o Phase IV
- Japan Virtual Clinical Trials Market, By
Region:
o Hokkaido
o Tohoku
o Kanto
o Chubu
o Kansai
o Chugoku
o Shikoku
o Kyushu
Competitive Landscape
Company Profiles: Detailed analysis of the major companies present in the Japan
Virtual Clinical Trials Market.
Available Customizations:
Japan
Virtual Clinical Trials market report with the given market data, Tech
Sci Research offers customizations according to a company's specific needs. The
following customization options are available for the report:
Company Information
- Detailed analysis and profiling of additional
market players (up to five).
Japan Virtual Clinical Trials Market is an
upcoming report to be released soon. If you wish an early delivery of this
report or want to confirm the date of release, please contact us at [email protected]